Summary for the Blog
- Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) is a tool that uses statistical analysis of historical data to help brands understand the impact of various marketing efforts on sales and revenue.
- MMM measures the influence of different variables, including advertising, trade promotions, pricing, distribution, and competition, to provide insights for budget allocation and sales forecasting.
- The benefits of using MMM include improved ROI, more accurate sales forecasts, and optimized marketing budgets.
- The limitations of MMM can include challenges with data quality, attribution, model complexity, and cross-channel integration.
The explosion of digital marketing has brought a massive influx of complex data, which, while valuable, can be overwhelming for brands. With technology gathering vast amounts of information, businesses often struggle to make sense of it.
A clear analytics strategy is essential to manage this data effectively and make informed decisions. Marketing mix modeling, for example, helps brands identify the best areas to invest their time and budget, ensuring more effective and efficient marketing efforts.
What is Marketing Mix Modeling?
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), sometimes known as Media Mix Modeling, is a tool that helps brands gauge the real impact of each marketing effort on key performance indicators (KPIs) like revenue, sales volume, and profit.
By analyzing these elements, companies can make informed decisions to fine-tune their marketing mix to meet sales targets. MMM offers data-backed insights that guide companies on how to best allocate their budgets across different marketing campaigns or channels, depending on how much each contributes to sales.
With MMM platforms, companies can streamline all marketing mix elements, like product, pricing, and promotions, and assess how each factor influences sales. In essence, the main aim is to estimate how much each marketing component contributes to overall business performance, helping companies pinpoint the most critical elements for their success.
Also read: Machine Learning Marketing
How Does Marketing Mix Modeling Work?
Marketing mix modeling relies on statistical analysis, typically using multi-linear regression, to reveal how different variables impact outcomes such as sales or engagement.
For instance, MMM can apply both linear and non-linear regression to assess how increasing investment in magazine ads has influenced overall sales. To gain the most accurate view of marketing effectiveness, it’s often beneficial to evaluate multiple models.
Data quality is essential, so dedicating time to gathering, consolidating, and cleaning data from internal databases, third-party sources, or a combination of both is key. MMM usually requires two to three years of historical data to account for factors like seasonality.
The results of MMM give marketers a clear numerical understanding of how different media channels contribute to their main goals, like driving conversions, boosting engagement, or something else. These insights help you measure ROI, inform budget allocation for future campaigns, and create accurate sales forecasts.
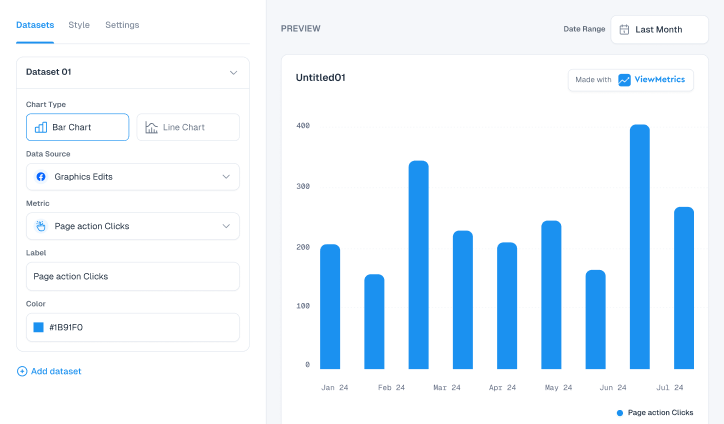
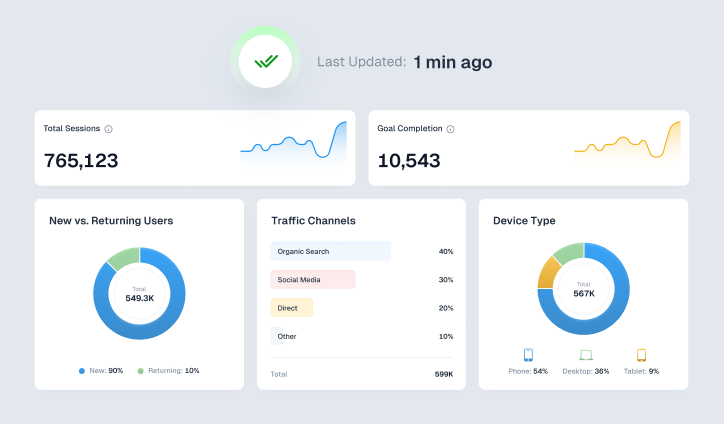
View All Your Marketing and Website Data - Instantly
Connect Instagram, Mailchimp, Google Analytics & more
Pre-built dashboards, no setup needed
Save hours on reporting every week
What are the Four Ps of Marketing Mix Modeling?
MMM focuses on the overall effect of marketing channels. However, the four Ps of marketing – Product, Price, Place, and Promotion – are what MMM considers the most when designing and evaluating marketing strategies.

With the help of marketing mix modeling, you can measure the effectiveness of your marketing efforts related to these elements.
What are the Elements Measured in Marketing Mix Modeling?
Several elements go into building an MMM model. These include:
- Base and Incremental Volume: When you mix different marketing activities together, you get base and incremental volume. This can be measured in marketing mix modeling.
- Advertising and Media: Evaluating the real influence of media on sales performance is extremely important. For this reason, the advertising and media metric helps the marketing team see how many people viewed or clicked on an ad or visited a promotional webpage and how many of these completed a purchase. It provides a clear snapshot of an ad’s effectiveness, offering valuable insight into its true impact on driving sales.
- Trade Promotions: Trade promotions play a key role in any marketing strategy, aiming to boost short-term sales through targeted promotion schemes that enhance product visibility and awareness.
- Pricing: Product pricing is crucial, and increasing it can significantly affect your sales. With MMM, you get an idea of the level of price elasticity you can choose to determine ideally how much percentage in prices you can alter without it majorly affecting your sales.
- Distribution: Marketing Mix Modeling can reveal the percentage change in distribution depth and reach across each channel and outlet.
- Launches: In a marketing model, existing variables are used to capture the extra volume driven by promotions during product launches, while specific variables measure the incremental impact of these launches.
- Competition: Competition variables are introduced to gauge how competing brands affect sales. Automated Marketing Mix Modeling utilizes cross-promotional and cross-price elasticity to respond to competitor strategies accurately.
Benefits of Marketing Mix Modeling
The marketing mix modeling has several advantages for your reporting models and brand analytics. Let’s delve into some:

- Improved ROI: Investing in effective marketing strategies allows businesses to see a stronger return on every dollar they spend.
- Insights Gathering: Marketing mix modeling offers valuable insights from business initiatives, helping teams make smarter budget decisions in marketing and sales. These insights can also be instrumental in showcasing the model’s benefits to stakeholders.
- Accurate Sales Forecasting: Sales forecasting involves predicting future revenue by analyzing the impact of past sales and marketing efforts. With marketing mix modeling, brands can identify which factors drive success, leading to more accurate revenue predictions.
- Historical Trends and Data Understanding: Marketing mix modeling focuses on analyzing past data gathered from various campaigns and initiatives, unlike many other analytics models that may overlook or only partially consider this information. The marketing mix model uncovers valuable insights for future strategies by thoroughly examining historical data and trends.
- Negative Impact Data Collection: Along with the positive impact, marketing mix modeling can also give you a clear picture of the negative impact your marketing efforts have created. This helps businesses get a clear picture of what to avoid with their next marketing strategy.
- Optimized Marketing Budgets: With MMM, brands and businesses get a clear idea of what marketing channels best suit them rather than just following the trend and spending money by trying out everything. This helps optimize your marketing budget, allocating it to channels that boost revenue and bring sales.
- Enhanced Marketing Campaigns: Marketing mix modeling helps the marketing team identify and prioritize what marketing campaigns and strategies are working the best. This leads to better budget planning and allocation for effective results.
Limitations of Marketing Mix Modeling
No doubt, marketing mix modeling brings advantages, but it also comes with challenges that can be overcome. Below are some limitations marketing teams can face with MMM:
1. Data Availablity and Quality
Getting accurate, reliable data isn’t always straightforward. Often, you’ll encounter incomplete entries, inconsistencies, or mistakes that make meaningful analysis a struggle. Plus, gathering information from various sources—like sales figures, marketing budgets, or market insights—and then combining these different data types can be a tricky task.
Solution: Invest in thorough data cleaning and quality assurance processes to keep your data accurate and dependable. Use validation methods to catch and correct errors early. To make your dataset even richer, consider adding supplemental data that brings in extra context and value.
2. Data Timeliness and Granularity
The detail and timing of data play a huge role in how accurate and effective your marketing mix modeling will be. When data is too broad—say, only available monthly or quarterly—it can mask valuable insights. Delays in accessing data can also hold back real-time decision-making.
Solution: Put controls in place to collect and process data with just the right level of detail. Invest in real-time data collection and processing tools so you’re equipped to make timely, informed decisions.
3. Attribution
Figuring out how marketing activities directly impact business outcomes isn’t easy. Things like time lags, seasonality, external factors, and the interplay between channels can make it tough to pin down the exact effects of specific marketing efforts. This can lead to ambiguity around which campaigns truly drive sales or conversions.
Solution: Try multi-touch attribution models that capture how each channel contributes to a conversion. For even deeper insights, consider advanced techniques like machine learning and causal inference to map out these causal relationships more precisely.
4. Model Interpretability and Complexity
Creating and understanding the statistical models used in marketing mix modeling, such as regression models and machine learning algorithms, demands specialized skills and can be hard for non-technical team members to grasp. Balancing simplicity with accuracy is a delicate task.
Solution: Use techniques like model simplification and feature engineering to keep models straightforward without losing predictive accuracy. Develop easy-to-understand visuals and explanations to help non-technical stakeholders fully grasp the results.
5. Cross-Channel Integration
Bringing together data and models from various marketing channels, like offline and online sources, can be tough because each uses different measurement methods, data formats, and attribution models. For a complete and accurate analysis, consistency and comparability across channels are crucial.
Solution: Set up standardized data collection and measurement practices across all channels. Build processes to integrate and harmonize data from different sources and consider unified attribution models that account for how different channels interact.
Also read: What is API Integration
6. Concerns with Compliance and Privacy
Working with sensitive customer data while staying compliant with privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA can be challenging for marketing mix modeling. It’s crucial to secure data, anonymize it, and follow legal guidelines to protect customer privacy and reduce legal risks.
Solution: Put strong data security measures in place to guard against unauthorized access. Apply anonymization techniques to strip out personally identifiable information and stay up-to-date on privacy regulations to ensure full compliance with the latest laws and standards.
How to Choose the Right MMM Tool or Software?
When selecting the best Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) software, a few factors stand out: your unique needs, budget, and how comfortable you are with technical tools. Let’s dive into some important things to consider:
1. Key Features and Functionality
- Data Integration: Make sure the tool can easily connect with your data sources, such as CRM systems, analytics platforms, or marketing automation software.
- Modeling Options: Opt for software that supports multiple modeling approaches, like regression analysis, time series, or machine learning, to meet your varied needs.
- Attribution Modeling: Check if the tool offers diverse attribution models—such as first click, last click, or U-shaped—to capture how each marketing touchpoint performs.
- Visualization & Reporting: Strong reporting features with clear visualizations are a must to help share insights with stakeholders effectively.
2. Usability Ease
- User Interface: A well-designed, intuitive interface can make modeling smoother and reduce the learning curve.
- Automation: Look for tools that automate routine tasks like data cleaning and model building to save time.
3. Scalability
- Data Capacity: Ensure the software can handle your data’s size and complexity.
- Model Sophistication: If you need complex or large-scale models, verify that the tool can support this.
4. Technical Requirements
- Compatibility: Confirm that the software works well with your current hardware and software setup.
- Deployment Option: Decide if you’d prefer a cloud-based tool for flexibility or an on-premise one for more control.
5. Budget
- Pricing Structure: Look at the software’s pricing model—whether it’s subscription or usage-based—and see if it aligns with your budget.
- Additional Costs: Consider extra expenses, like charges for data storage, customer support, or professional assistance.
6. Vendor Support
- Customer Support: Check the vendor’s reputation for customer service to see if they provide timely help.
- Training Resources: Access to training and documentation can make a big difference in how quickly you get up to speed with the software.
7. Proof of Concept
- Trial or Demo: Request a trial or demo to see firsthand if the tool meets your needs.
With these considerations in mind, you’ll be well-equipped to choose the MMM software that best aligns with your objectives.
View All Your Marketing and Website Data - Instantly
Connect Instagram, Mailchimp, Google Analytics & more
Pre-built dashboards, no setup needed
Save hours on reporting every week
Frequently Asked Questions About Marketing Mix Modeling
What is the difference between MMM and attribution modeling?
MMM looks at the bigger picture, assessing how all marketing channels work together to drive sales. On the other hand, attribution modeling dives into the specifics, giving credit to each individual marketing interaction along the customer journey.
What is an example of marketing mix modeling?
One typical use of MMM is by retailers who apply it to figure out the best balance between in-store promotions, online ads, and loyalty programs. By understanding how each channel influences sales, they can better allocate their budgets and boost their return on investment. Another example is a consumer goods company analyzing the success of TV ads, digital marketing, and PR campaigns. MMM helps pinpoint which channels generate the most sales and which might need more attention to improve performance.